Overview
CLLT develops computational frameworks for measuring and analyzing linguistic distance between languages and language varieties. Our work combines theoretical linguistics with quantitative methods to understand language change, dialectal variation, and historical relationships.
By creating rigorous, multi-dimensional measures of linguistic distance, we provide tools for historical linguistics and typology.
Multi-Dimensional Framework
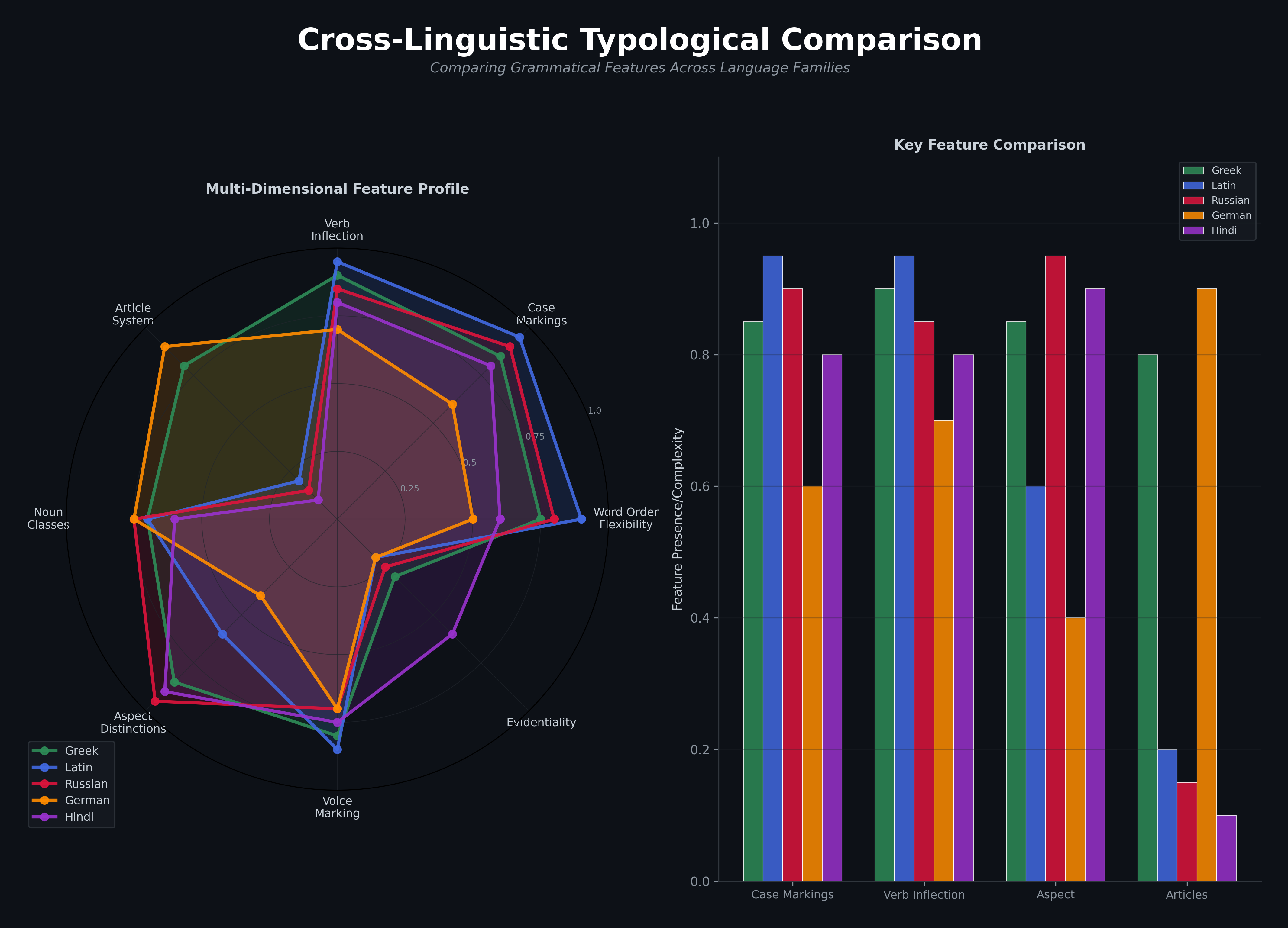
Multi-Dimensional Distance Metrics
We have developed a comprehensive framework for analyzing linguistic distance across Indo-European languages. This framework moves beyond simple lexical similarity to capture:
- Phonological Distance: Sound system changes and correspondences
- Morphological Distance: Inflectional and derivational patterns
- Syntactic Distance: Word order and structural differences
- Lexical Distance: Vocabulary divergence and cognate retention
- Semantic Distance: Meaning shifts and semantic change
- Orthographic Distance: Writing system divergence

Computational Methods
Our research employs both traditional linguistic analysis and modern computational techniques:
- Quantitative Typology: Statistical analysis of typological features
- Corpus-Based Analysis: Large-scale analysis of authentic linguistic data
- Machine Learning: Automated feature extraction and pattern detection
- Information-Theoretic Measures: Entropy-based distance metrics
Applications to Indo-European Languages
Our framework has been applied to analyze relationships within the Indo-European family, providing new insights into:
- Historical development of Greek and its dialectal branches
- Comparative distance between major Indo-European branches
- Rates of linguistic change across different linguistic levels
- Contact-induced change versus inherited features
Research Impact
Dialectology
Quantifying relationships between dialectal varieties and tracking dialect change over time
Historical Linguistics
Modeling language change and reconstructing historical linguistic relationships
Language Typology
Cross-linguistic comparison and typological classification based on multiple dimensions
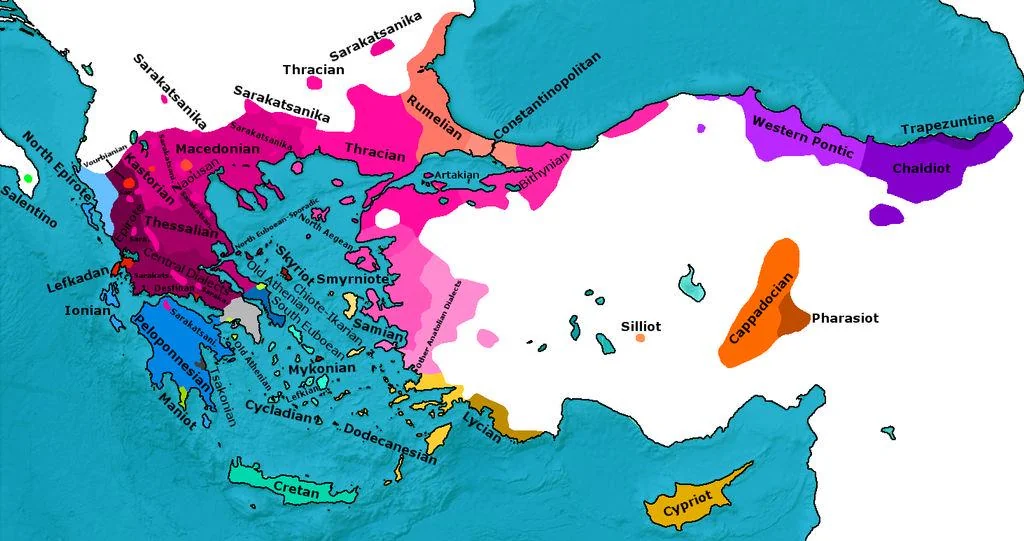
Greek Dialectal Studies
A particular focus of our distance studies work is the analysis of Modern Greek dialects:
- Measuring distance between Standard Modern Greek and dialectal varieties (Cypriot, Pontic, Cretan, Northern)
- Tracking convergence and divergence patterns in Greek dialectology
- Understanding the impact of standardization on dialectal variation
- Computational methods for dialect identification and classification
This work directly informs our NLP research on Greek dialects, providing theoretical grounding for computational models of dialectal variation.
Future Directions
Ongoing and future work includes:
- Extending the framework to additional language families
- Integration with neural language models for distance estimation
- Development of interactive visualization tools for linguistic distance
- Application to sociolinguistic variation and language contact scenarios
- Creating open datasets for linguistic distance research